Quail eggs have become an unexpected but valuable resource for scientists seeking to gain a deeper understanding of fetal development and the causes of birth defects. The unique properties of avian eggs make them conducive to studying embryos in real-time, allowing researchers to observe critical processes that were previously only understood through static images.
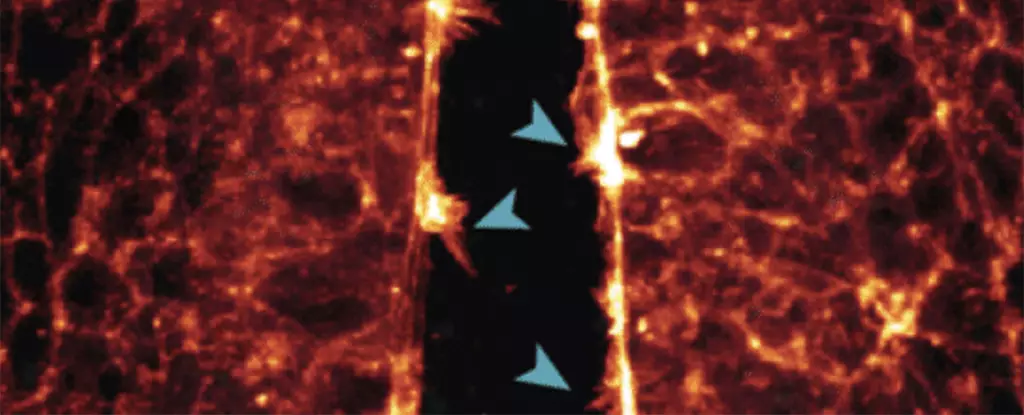
A groundbreaking study conducted in Australia utilized quail eggs engineered to express a fluorescent peptide that binds to actin proteins in the embryo’s cytoskeleton. This innovative approach enabled the researchers to observe the intricate formation of organs such as the heart, brain, and spinal cord at a level of detail previously unattainable. By capturing the movement of cells in real-time, the team gained valuable insights into how these structures develop and interact during the early stages of embryonic growth.
One of the key observations made during the study was the process of neural tube closure, a critical stage in central nervous system development. By tracking the movement of cells and their protrusions as they joined together to form the neural tube, researchers were able to identify potential mechanisms underlying defects that can lead to brain and spinal cord abnormalities in human embryos. Similarly, the study revealed the intricate process by which heart stem cells establish connections, shedding light on the mechanisms that govern heart development in avian embryos.
Understanding the cellular interactions and processes that occur during early development is crucial for identifying and potentially mitigating the risk of birth defects. By studying the biological transformations that take place at the smallest scales in real-time, researchers hope to uncover new insights that could inform future strategies for preventing congenital abnormalities. The implications of this research extend beyond the laboratory, offering hope for improving prenatal care and promoting healthier pregnancies in the future.
The success of the study using quail eggs as a model for embryonic development has paved the way for additional research projects aimed at uncovering the genetic and molecular factors that influence fetal growth. By identifying key proteins or genes that play a role in the development of organs and tissues, researchers hope to develop targeted interventions for preventing or screening for birth defects. The ongoing advancements in this field hold promise for enhancing our understanding of prenatal development and ultimately improving outcomes for both mothers and infants.
The use of quail eggs in studying early development represents a significant advancement in the field of developmental biology. Through high-resolution imaging and real-time observations, researchers are gaining unprecedented insights into the intricate processes that shape embryonic growth. By leveraging this knowledge to inform future research and clinical practices, we have the potential to transform the way we approach prenatal care and support healthy pregnancies.

Leave a Reply