In recent years, abnormally warm patches of water in the Pacific Ocean, known as ‘blobs’, have been causing havoc on marine ecosystems. These warm patches have been linked to a reduction in aerosol emissions in China. This connection has been discovered through a new study conducted by an international team of researchers, using detailed computer simulations to understand the effects of aerosol emissions on the environment.
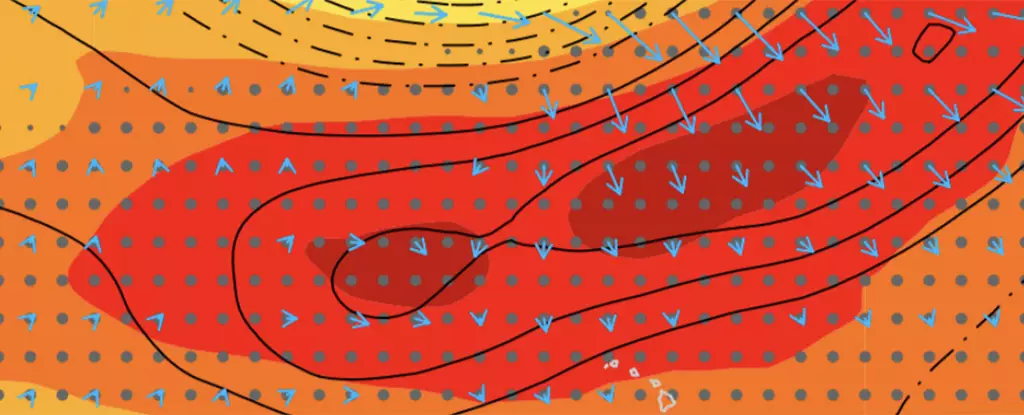
The researchers found that the reduction in aerosol emissions in China has triggered atmospheric circulation anomalies beyond its source region. This has resulted in a substantial mean surface warming in the Northeast Pacific, creating a favorable condition for extreme ocean warming events. The rapid abatement of aerosols in China has led to a significant rise in temperatures in the Pacific Ocean, exacerbating the already existing issue of global warming.
These ‘blobs’ in the Pacific Ocean have had devastating effects on marine life, causing the deaths of fish, seabirds, and other organisms on a massive scale. Additionally, toxic algae blooms have further damaged ecosystems by blocking sunlight and consuming oxygen. The delicate balance of marine ecosystems is being disrupted by the warming trends caused by aerosol emissions reductions in China.
Complex Meteorological Systems at Play
It is not just the direct radiative effects of aerosols that are contributing to the warming of the Pacific Ocean. The researchers suggest that a chain reaction of warming, due to the absence of aerosols, has shifted weather systems, reducing wind speeds over specific regions in the Pacific. This has resulted in patches of ocean overheating to an even greater degree. The intricate interactions of various factors in the atmosphere are leading to the creation of these warm patches in the ocean.
Need for Understanding and Action
The findings of the study shed light on the mechanisms behind ocean-atmosphere changes in the North Pacific, emphasizing the importance of considering the risks associated with a reduction in anthropogenic aerosol emissions when assessing climate change impacts. As our planet continues to warm, it is crucial to understand the intricate balances and factors at play to mitigate the detrimental effects on marine ecosystems and the environment as a whole.
The reduction in aerosol emissions in China has been linked to the appearance of ‘blobs’ in the Pacific Ocean, causing significant warming and disruptions to marine ecosystems. The interconnected nature of these environmental processes highlights the need for further research and action to address the consequences of aerosol emissions on our planet. As we strive to combat climate change, understanding the complex interactions between aerosols, atmospheric circulation, and ocean temperatures is essential in shaping effective environmental policies for a sustainable future.

Leave a Reply