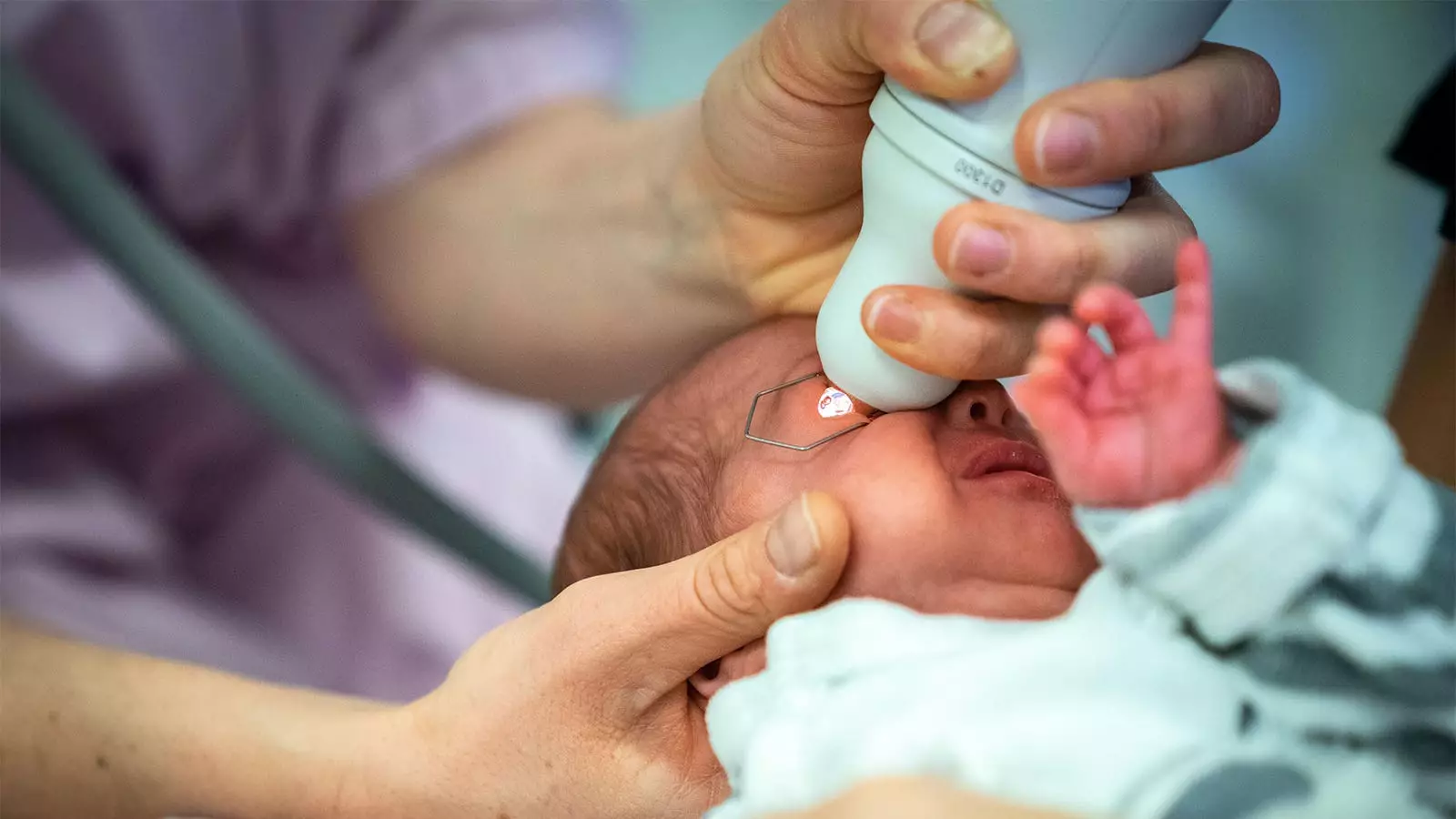
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) screening is a critical procedure that involves careful eye examinations for preterm infants, who are at high risk of developing severe vision problems. Recent research led by Dr. Asimina Mataftsi and her colleagues has brought to light an important advancement in the administration of mydriatic agents during these procedures. Their findings affirm that mydriatic microdrops offer significant benefits over conventional mydriatic drops while minimizing the risks often associated with their use, thus heralding a potential evolution in clinical practice.
Standard mydriatic drops have long been employed to facilitate ocular dilation in neonatal examinations. However, the systemic effects of these medications on preterm infants raise substantial concerns. Due to their low body mass and immature metabolic systems, preemies are particularly vulnerable to adverse reactions. Previous evidence has indicated a correlation between using standard drops and adverse respiratory and cardiovascular events, which may manifest as apnea episodes, varying oxygen saturation levels, and gastrointestinal complications. The pressing need for safer alternatives in this delicate patient population cannot be overstated.
In a recent randomized control trial involving 83 preterm infants, mydriatic microdrops were demonstrated to be noninferior to standard drops in achieving adequate dilation. Interestingly, microdrops not only matched the traditional drops’ effectiveness at intervals of 90 and 120 minutes but outperformed them at the 45-minute mark. This is particularly significant, as timely and effective dilation is essential for accurate ROP screening. Furthermore, microdrops were associated with lower incidences of adverse effects, including lower rates of hypertensive events and more stable oxygen saturation readings post-administration.
These results are promising as they suggest that lower volumes of mydriatic agents maintain adequate ocular responses without the accompanying systemic dangers linked to standard administrations. The study’s authors noted the need for future research to explore the efficacy of various regimens further and to ensure that these findings can be generalized across broader populations.
The implications of using mydriatic microdrops for ROP screening extend beyond merely enhancing clinical outcomes. By adopting a protocol that incorporates microdrops into practice, healthcare providers can shift away from methods associated with significant adverse effects. This can lead to improved overall health outcomes for vulnerable infants — a prospect that can motivate further changes in clinical guidelines and protocols.
Shifting this clinical paradigm is particularly crucial given that numerous anecdotal reports indicate that some infants exhibit adverse reactions after standard ROP screenings. These voices, alongside emerging research data, form a compelling case for the adoption of microdrops, especially when considering the safety of the most fragile patients.
While the study conducted by Mataftsi et al. provides valuable insights into the use of mydriatic microdrops, it is essential to recognize its limitations. Notably, the absence of comprehensive safety outcome data for a portion of the study population underscores the need for larger, multicenter trials to validate these findings. Additionally, exploring the long-term effects of microdozing and establishing standardized protocols will be paramount to generalizing these findings.
Conclusively, the advancement represented in the shifting from standard mydriatic drops to microdrops serves as a critical step toward enhancing neonatal care. This evolution reflects an ongoing commitment to refining practices that not only aim for clinical efficacy but also prioritize the well-being of the most vulnerable patients in our healthcare system. With continued research, we can better understand the benefits, limitations, and overall systemic exposure associated with this promising alternative.

Leave a Reply